The content of the article:
The room where oyster mushrooms grow is called differently in different countries. In addition to the term growing room, I know such names as cultivation chamber or growing chamber, cultivation tent and fruiting room.
Therefore, I will use some of these names, referring to the room for oyster mushrooms.
There are quite a few ways to distribute the air flow in oyster mushroom chambers, since there is no generally accepted standard.
The main directions are air exchange with and without air ducts (Tornado system).
I prefer the proven air movement pattern that is used in champignon (button mushrooms) cultivation and adapted for oyster mushroom cultivation:
Consider how to make air supply and exhaust in the growth chamber.
If the ventilation system in your cultivation chamber consists of a hole in the wall that allows air to come in and an exhaust fan that pulls the air out, you can read about that at the very bottom of this article.
The flow moving through the ventilation system must have certain parameters (specific values depends on mushroom strain):
Air exchange for oyster mushrooms is not calculated in air volumes per hour, but is calculated by the amount of substrate loaded into the cultivation chamber.
The amount of air required is calculated in cubic meters per ton of mushroom blocks.
The air exchange fan must be centrifugal.
In growing chambers up to 15 tons of substrate, both a duct centrifugal fan and a snail fan can be installed.
In rooms with 20-50 tons of substrate, a snail fan is required.
With intensive loading of grow rooms (from 160 to 200 kg per square meter) and simultaneous fruiting (with a single-zone method), the throughput of the fan is calculated based on an air flow of 300 cubic meters. per 1 ton of substrate. If there are blocks of different ages in the room, and simultaneous fruiting of all batches does not occur, 180-220 cubic meters / ton are taken for calculation.

The diameter of the central and side air ducts is calculated according to the formulas, based on the fact that the speed of air movement in them should be 4-5 m/s.
Those air ducts are made of tin, which are located before the blowing fan and suck in outside and recirculated air.
They must be the same diameter as the central distribution duct.
The central air duct has the largest diameter, and the distribution (side) duct has a smaller diameter.
The formula takes into account the capacity of the fan and the number of side air ducts.
For chambers no longer than 16 meters, I made a ventilation calculator in Excel.
There are also ready-made ventilation calculations for growing chambers filled with up to 8 tons of substrate, the maximum area of the growing chamber is approximately 120 square meters.

Why not just make holes in air ducts, but put nozzles?
This is done to create directed jets of air and increase their speed.
Disposable plastic cone cups do a great job of this function.
The distance between the nozzles-cups is from 0.45 cm to 80 cm.
First, according to the formula, the total number of cups is calculated and their diameter is determined - a certain amount of air per hour must pass through the total cross section of all holes.
And then, knowing the total length of the side air ducts, the distance between the nozzles is calculated.
The speed of the jet from the nozzle is 8-9 m/s. With intensive loading of chambers (especially with a single-zone method), the air flow per hour increases, and the speed can be up to 12 m/s.
The recirculation pipe is the pipe that takes air from the growing chamber and feeds it into the ventilation system. It is located in front of the heat exchanger (water heater) and the fan. This pipe goes into another pipe, which also includes a fresh air pipe. There the air is mixed and supplied to a heat exchanger or cooler, after which a fan is located.
Thus, microclimate jumps are smoothed out - after all, the air from the growing chamber is already heated and humidified to the required parameters. Recycling significantly reduces the cost of mushroom production in winter.
After all, oyster mushroom does not need a large amount of fresh air as much as well-organized high-speed streams.
There is a damper on the pipe that supplies air from the growing room to the ventilation system.
The percentage of opening of this damper depends on the number of mushrooms simultaneously bearing fruit in the growing chamber. The second damper is located in the fresh air pipe.
The more one damper is open, the less the other is open. In this way, we regulate the air supply from outside, depending on the condition of the mushrooms.
A air filter is installed on the recirculation pipe to clean the flow that enters the system from fungal spores. Otherwise, the fan blades and water air heater lamellas will clog and work worse.
The air filter must be class G3 to catch dust and oyster mushroom spores.
Air heating takes place only in the ventilation system.
In the growing room, the air cannot be heated with radiators, heat guns, buleryan!
The water air heater is built into the ventilation tin pipes in the area after mixing the indoor air from the fruiting chamber and fresh air, always before the fan.
Learn more about space heating.
The exhaust must remove all outside air that enters the room. If the exhaust (hood) is weak, the blower fan will not supply the calculated amount of air, but less. The flow rate will drop, which may adversely affect the shape and condition of the oyster mushroom fruiting bodies.
The power of the mushroom exhaust fan is about 90% of the blower.
If the fresh air damper is open 100%, the exhaust fan should operate at full power.
When using recirculation, the speed of the exhaust fan must be controlled by a frequency converter or damper so that it sucks in as much air as the supply air damper is open.
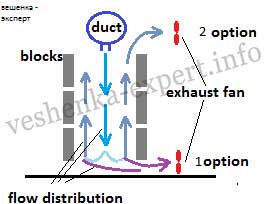 The exhaust must be placed at the top! Carbon dioxide does not accumulate at the bottom near the floor.
The exhaust must be placed at the top! Carbon dioxide does not accumulate at the bottom near the floor.
It is a myth. In a chamber where ventilation works, this is impossible - carbon dioxide is not a brick that has fallen and lies on the floor. It mixes with the air flow.
The mushroom exhaust fan should be placed 15-20 centimeters lower than the supply fan. See picture for option 2.
When the flow from the duct goes down, it partially captures the secretions from fungal drusen. If the exhaust pipe is at the bottom (option 1), the air immediately goes into this hole.
If the hood is located at the top, the air, hitting the floor, goes under the ceiling, between the downdraft and the blocks, and removes the vapors from the oyster mushroom.
Since mushrooms need air fully prepared, moisture should enter the air only in air ducts.
That is, humidifiers must be built into the ventilation system.
If there are mushrooms in the room - all the time!
You can not turn on ventilation and humidification on a timer, two hours after two or other intervals - this should not be.
Otherwise, you will not get a stable microclimate, increase humidity and temperature fluctuations.
The exhaust fan, as well as all ventilation, must always be running in the grow room if the fresh air damper is open. If the system is in 100% recirculation mode, then the exhaust fan is turned off.
Air mixing in a grow chamber without air ducts
If you need such ventilation, or need advice on how to make it effective, contact me for advice.
Ventilation in the growing chamber should ALWAYS work, creating a certain, stable microclimate.
The energy savings associated with periodically turning off the fans and humidification system do not justify the loss in yield.
Due to jumps in microclimatic parameters (temperature, humidity, CO2), the fruiting bodies of oyster mushrooms are deformed, and yield losses can reach 5-10% in two waves (flush).
